TBX6基因罕见突变联合常见亚效等位基因导致先天性脊柱侧凸的遗传学模型
- 新闻
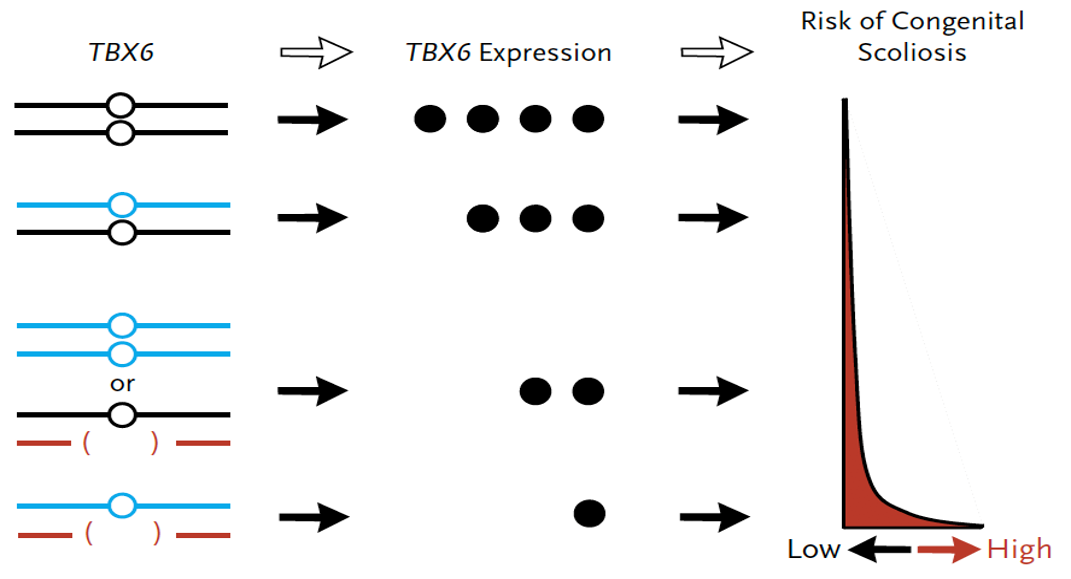
Generally, the molecular mechanism of human mendelian disorders associated with heterozygous gene deletions or null mutations is haploinsufficiency, in which half the gene dosage is not sufficient for normal function. In contrast, the effect of diminished TBX6 dosage in congenital scoliosis is complex. We found that an additional TBX6 hypomorphic allele is required to cause a further decrement in gene-expression dosage beyond haploinsufficiency for penetrance of the congenital scoliosis phenotype.